Is it illegal to not have a disabled toilet UK
The legal requirements for disabled toilets in the UK are a critical consideration for public and commercial establishments. This article aims to offer an informative overview of disabled toilets, encompassing their definition and purpose, and outlining the implications of non-compliance with the regulations.
Additionally, exceptions and exemptions to the law will be examined, along with strategies for retrofitting existing toilet facilities to accommodate disabled individuals effectively. The article will also highlight the advantages of providing disabled toilets and elucidate the potential legal ramifications, including enforcement actions and fines for failure to adhere to the prescribed standards.
Overview of Disabled Toilets in the UK
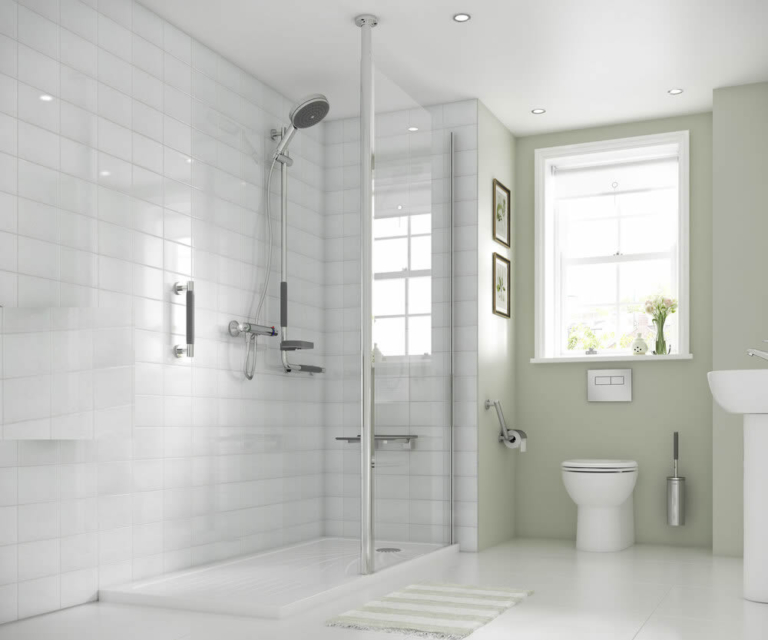
Accessible toilets in the United Kingdom are crucial elements of public facilities carefully designed to ensure access for individuals with disabilities. These facilities comply with strict accessibility standards with the aim of providing a dignified toilet experience for all individuals.
Definition and Purpose
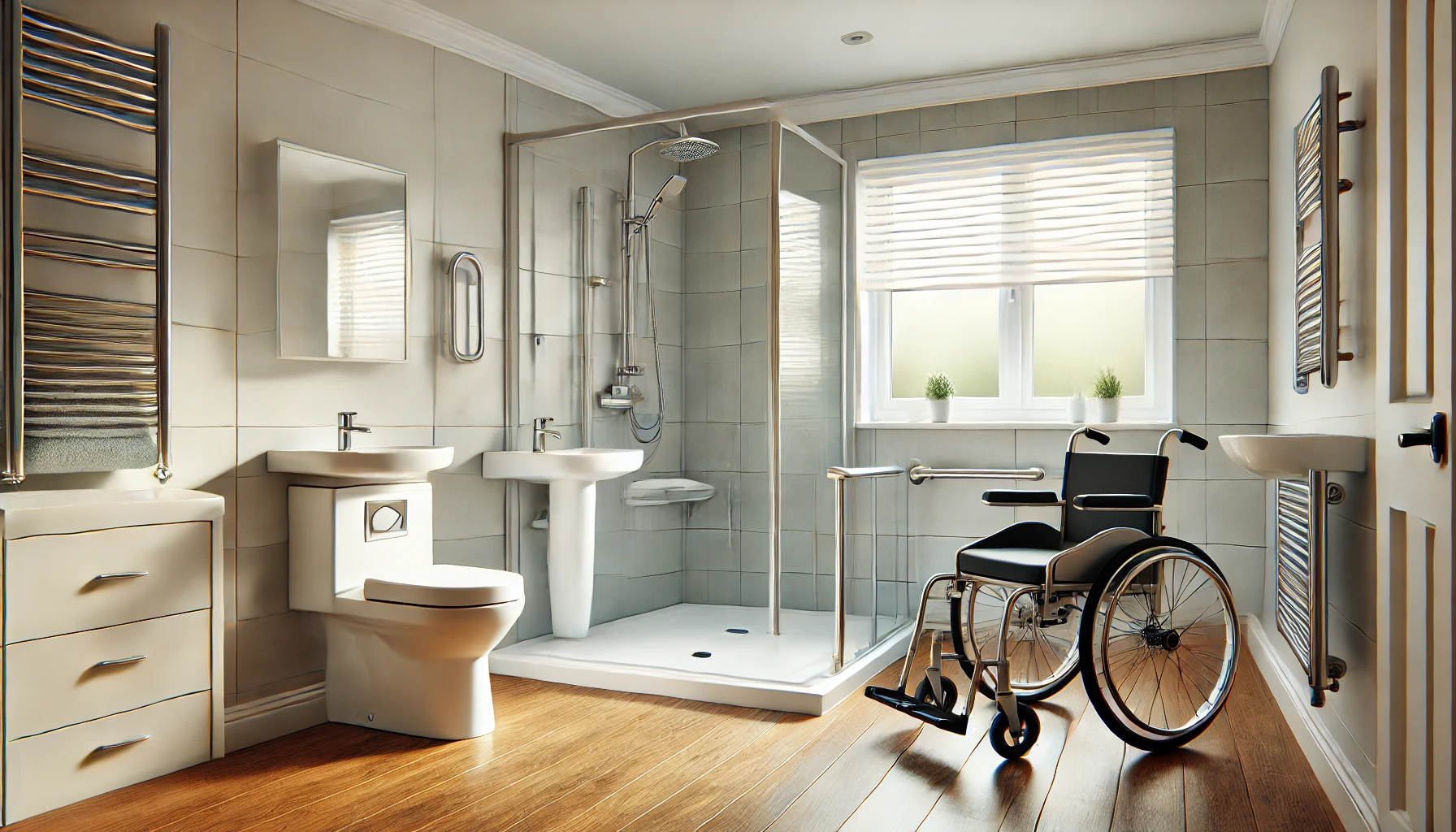
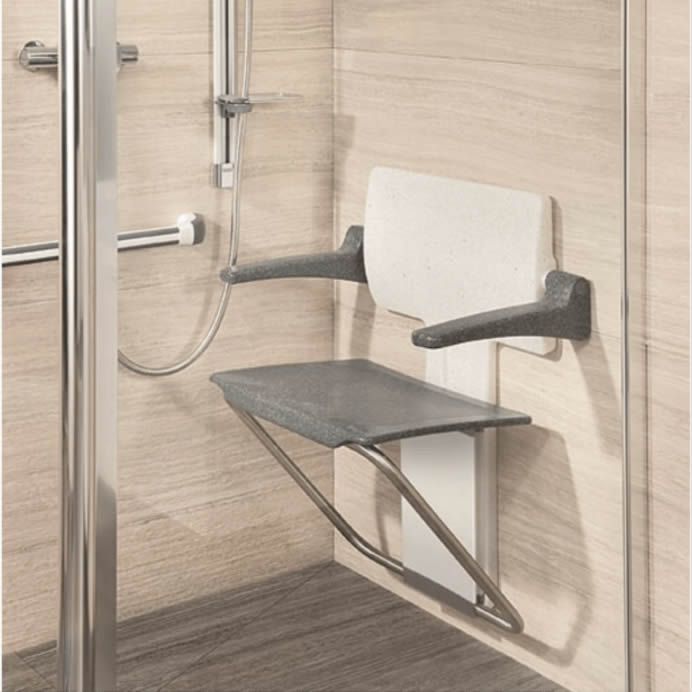
An accessible toilet is defined as a facility that is specifically tailored to meet the needs of individuals with disabilities, providing them with convenience and comfort. Critical design elements that enhance the accessibility of these toilet facilities include strategically positioned grab rails for support and stability, wider doorways to accommodate wheelchair access, and emergency call buttons for immediate assistance. These features not only improve the overall usability of the toilet but also foster independence and safety for individuals in need of disabled access provisions. The layout and positioning of fixtures like basins, WCs, and hand dryers are meticulously planned to ensure optimal functionality for all users.

Legal Requirements for Disabled Toilets
In the United Kingdom, the legality and regulations concerning accessible toilets are overseen by a combination of disability rights laws, building codes, and the Equality Act 2010. These regulations demand compliance with specific accessibility standards to ensure equal access for all individuals.
UK Laws and Regulations
The principal legislation governing disabled access in the UK is the Equality Act 2010. This Act establishes definitive guidelines and regulations aimed at ensuring that public facilities, including toilet facilities, are easily accessible to individuals with disabilities. According to the provisions of the Equality Act 2010, service providers are legally obliged to make reasonable adjustments to facilitate access for disabled individuals. These adjustments may involve modifying physical structures that pose barriers, providing auxiliary aids and services such as Braille information, or adapting communication methods.
Furthermore, the Act prohibits discrimination on the grounds of disability, thereby requiring that businesses, public establishments, and transport services must make necessary adjustments to comply with legal requirements. Oversight and enforcement of these laws fall under the purview of the Equality and Human Rights Commission, an organisation dedicated to combating discrimination and advocating for equality among all individuals.
Consequences of Not Having a Disabled Toilet
The lack of a disabled toilet in public facilities can lead to serious consequences, including legal action, financial fines, and damage to reputation. It is crucial for organisations to comply with their legal obligations in line with UK accessibility standards.
Potential Legal Action and Fines
Businesses that do not fulfil their obligations regarding disabled access, which includes the provision of accessible toilet facilities, may encounter legal ramifications and significant financial penalties due to their failure to adhere to regulations in the United Kingdom.
For example, within the UK, enterprises discovered to have neglected the requisite adjustments for individuals with disabilities may be liable for fines amounting to as much as £30,000. Affected persons or advocacy organisations hold the ability to pursue legal recourse to compel adherence to accessibility statutes. Given these considerations, it is imperative for organisations to place a high emphasis on accessibility in order to avert potential legal repercussions and safeguard the rights of individuals with disabilities.
Exceptions and Exemptions
In the United Kingdom, the disabled access regulations are characterised by their stringent nature. However, there exist particular circumstances in which the provision of a disabled toilet may not be feasible. These exceptions and exemptions are typically attributed to constraints related to building structure or financial limitations.
When a Disabled Toilet is Not Required
There are instances where exemptions from disabled access obligations may be considered if the installation of a disabled toilet is structurally unfeasible or poses a significant financial burden. However, it is imperative to explore alternative accommodations to address the needs of individuals with disabilities.
For instance, if the layout or age of a building renders the installation of a traditional disabled toilet unachievable, a deviation from the standard requirements could be granted. In such scenarios, building owners may need to consider alternative solutions, such as providing a unisex toilet equipped with grab rails and adequate space for wheelchair users. These alternative accommodations must adhere to construction standards to ensure reasonable access for persons with disabilities while also meeting essential safety and functional criteria.

Making Existing Toilets Accessible
Adapting current toilet facilities to accommodate disabled individuals involves adhering to precise accessibility standards and disabled access specifications to ensure safety and convenience.
Adapting Toilets for Disabled Individuals
The process of making toilets accessible for disabled individuals necessitates meticulous planning and strict adherence to the washroom conforms to all accessibility and safety regulations. This includes implementing specific adaptations such as strategically placing grab rails for support, widening doorways to facilitate wheelchair access, and adjusting basin heights to accommodate individuals with mobility restrictions.
Considering disabled access considerations is paramount in the creation of an inclusive washroom that addresses the varied needs of all individuals. By adhering to these guidelines and incorporating these modifications, a substantial improvement in accessibility and inclusivity within washroom facilities can be achieved.
Benefits of Having a Disabled Toilet
The provision of a disabled toilet in public spaces presents a range of advantages, such as enhanced accessibility and inclusivity. This initiative aligns with equality legislation, guaranteeing that individuals of all abilities enjoy equitable access to toilet facilities.
Improving Accessibility and Inclusivity
Enhancing accessibility and inclusivity in public facilities by providing accessible toilets is essential for enabling individuals with disabilities to actively participate in social, economic, and cultural endeavours. This strategy not only benefits the disabled community but also cultivates a more inclusive environment for all individuals.
The presence of accessible lavatories in public facilities signifies a commitment to equality and diversity, facilitating the removal of physical barriers that might obstruct individuals from fully engaging in daily activities. By recognising the diverse needs of all individuals, society at large becomes more empathetic and understanding.
The creation of accessible spaces also nurtures a sense of belonging and acceptance, contributing to an atmosphere where everyone feels valued and respected.